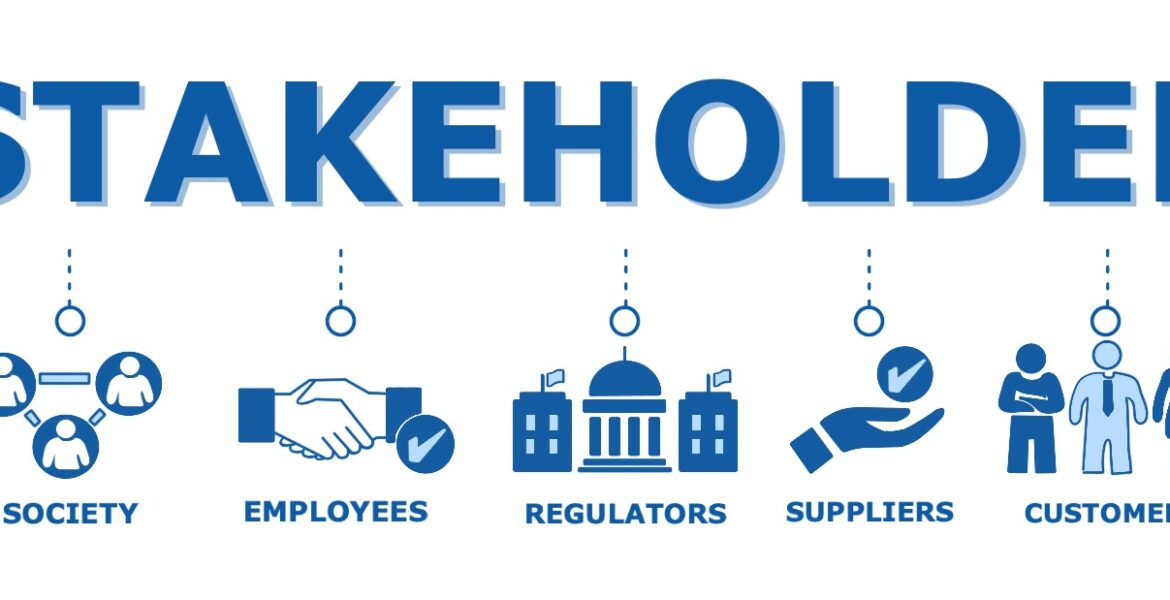
Why Is Stakeholder Management Important
In the realm of business and project management, stakeholders are the key players who can significantly influence the success or failure of a venture.
Stakeholder management is a critical process that aims to identify, analyse, and engage with individuals, groups, or organizations that have an interest in or are impacted by a project.
Effectively managing stakeholders can be the difference between a smooth and successful project delivery or encountering challenges and roadblocks along the way.
Stakeholder management is of paramount importance for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in gaining a comprehensive understanding of the project’s requirements and expectations from the various parties involved.
By engaging with stakeholders at the early stages of a project, business analysts and project managers can gather essential insights, identify potential risks, and define clear project objectives.
This understanding forms the foundation upon which the project can be planned, executed, and monitored effectively.
Secondly, stakeholder management fosters collaboration and builds strong relationships with the individuals and groups who have a vested interest in the project’s outcome.
It ensures that the lines of communication remain open, enabling stakeholders to express their concerns, provide feedback, and offer valuable suggestions.
By actively involving stakeholders throughout the project’s lifecycle, business analysts can maintain transparency and keep them informed about the project’s progress and any changes that may arise.
A critical aspect of stakeholder management is identifying and prioritizing stakeholders based on their level of influence and interest in the project.
This process allows business analysts and project managers to allocate resources effectively and tailor communication strategies to suit each stakeholder’s needs.
Understanding the varying perspectives and interests of stakeholders helps in managing expectations and addressing potential conflicts proactively.
Moreover, effective stakeholder management can significantly impact the project’s success by gaining stakeholder buy-in and support.
When stakeholders feel heard, respected, and valued, they are more likely to champion the project and contribute to its success.
Their support can translate into valuable endorsements, securing necessary resources, and even generating positive word-of-mouth referrals for the project.
Stakeholder management is particularly crucial in complex projects or those with multiple stakeholders with diverse interests and needs.
Without proper management, projects can encounter delays, misunderstandings, and even outright resistance, leading to wasted resources and missed opportunities.
To implement effective stakeholder management, business analysts should employ a structured approach that includes the following key steps:
Stakeholder Identification

Stakeholder identification is a critical step in effective stakeholder management. It involves systematically identifying all individuals and groups who have an interest in or may be impacted by a project.
This includes not only internal stakeholders such as employees and management but also external stakeholders like customers, suppliers, regulatory authorities, and the community.
Identifying stakeholders helps business analysts and project managers to understand the project’s broader impact and tailor their strategies accordingly.
For instance, consider a business analyst working on a software development project for a financial institution. In this scenario, stakeholders may include the bank’s management team, IT department, end-users (bank staff and customers), compliance officers, and external auditors.
Each stakeholder group may have distinct needs, expectations, and concerns related to the project.
By conducting thorough stakeholder identification, the business analyst can categorize and prioritize stakeholders based on their influence and impact on the project.
To successfully identify stakeholders, the business analyst can follow these steps:
- Gather Relevant Information: Conduct interviews, surveys, and research to gather information about potential stakeholders. Consult with project sponsors, team members, and subject matter experts to ensure a comprehensive list.
- Categorize Stakeholders: Group stakeholders based on their level of influence, interest, and power. This helps in understanding their varying degrees of impact on the project and facilitates targeted engagement strategies.
- Analyse Stakeholder Interests: Understand the needs, concerns, and expectations of each stakeholder group. This insight helps in tailoring communication and addressing potential conflicts proactively.
- Validate the List: Share the stakeholder list with relevant team members and stakeholders to ensure all key individuals and groups are included and that there are no omissions.
By investing time and effort in stakeholder identification, business analysts can set the foundation for successful stakeholder management.
This process lays the groundwork for effective communication, engagement, and collaboration throughout the project lifecycle, ultimately contributing to project success and stakeholder satisfaction.
Stakeholder Analysis
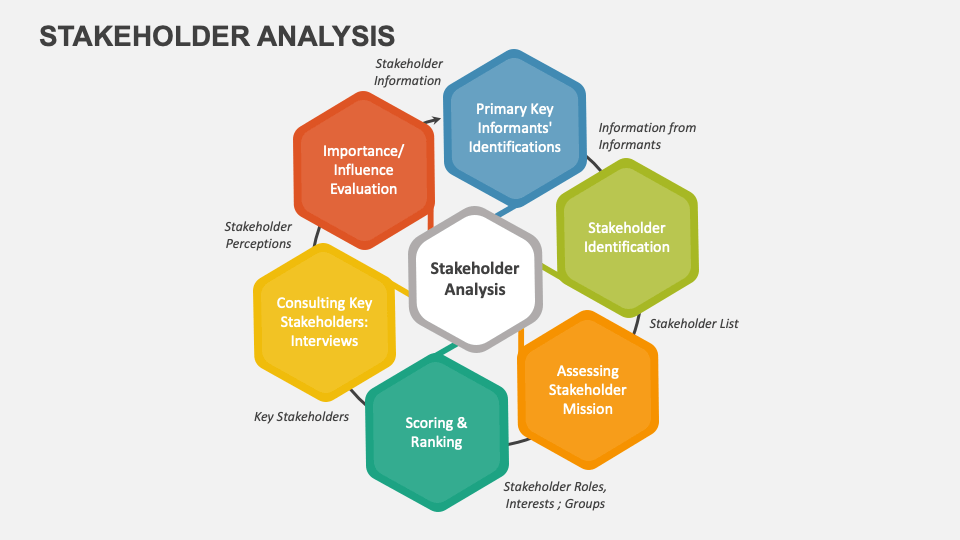
Stakeholder analysis is a fundamental process in effective stakeholder management. It involves a comprehensive examination of the interests, concerns, and potential impact of each stakeholder on a project.
By understanding the varying degrees of influence and interest, business analysts can categorize stakeholders based on factors like power, level of interest, and attitude towards the project.
This analysis is crucial for developing targeted communication strategies, fostering positive relationships, and mitigating potential risks and conflicts.
Let’s consider a real-life scenario where stakeholder analysis played a crucial role.
Imagine a business analyst working on a large-scale infrastructure development project in a city.
The stakeholders in this project are numerous and diverse, ranging from government officials and local residents to construction companies and environmental activists. The business analyst conducts stakeholder analysis by engaging in the following steps:
- Identify Stakeholders: Compile a comprehensive list of all stakeholders involved in the infrastructure development project, ensuring that all relevant parties are considered.
- Analyse Interests and Concerns: Conduct interviews, surveys, and meetings with each stakeholder to understand their interests, concerns, and expectations related to the project. This analysis helps in identifying potential areas of alignment and conflict.
- Categorize Stakeholders: Group stakeholders into categories based on their power and level of interest in the project. For example, high-power stakeholders with high levels of interest may require more frequent communication and involvement.
- Develop Communication Strategies: Tailor communication strategies for each stakeholder category, taking into account their specific interests and preferred communication channels.
- Address Concerns and Mitigate Risks: Based on the stakeholder analysis, proactively address any concerns or potential risks to ensure that the project progresses smoothly.
By conducting a thorough stakeholder analysis, the business analyst can establish a solid foundation for effective stakeholder management throughout the project’s lifecycle.
This process enables the project team to engage stakeholders in a meaningful way, ensure their needs are considered, and ultimately lead to the successful completion of the infrastructure development project.
Communication Plan

Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful stakeholder management.
Developing a comprehensive communication plan is vital for ensuring that stakeholders are engaged throughout the project and well-informed about its progress.
The business analyst plays a crucial role in creating this plan, which outlines the strategies for communication, the frequency of engagement, the types of information to be shared, and the appropriate communication channels to be used.
Let’s consider a real-life scenario where a business analyst was tasked with implementing a new software system for a company.
The stakeholders involved in this project included employees from various departments, managers, and the executive team.
To address their diverse needs and ensure smooth adoption of the new system, the business analyst followed these steps to develop a communication plan:
- Stakeholder Analysis: The business analyst conducted stakeholder analysis to identify the interests, concerns, and expectations of each stakeholder group. This analysis helped in understanding the varying communication preferences and needs.
- Communication Channels: Based on the stakeholder analysis, the business analyst determined the most effective communication channels for each group. For example, regular team meetings were scheduled for department employees, while high-level presentations were organized for the executive team.
- Information Sharing: The communication plan outlined the type of information that would be shared at different stages of the project. This included updates on project milestones, training schedules, and opportunities for feedback and input.
- Engagement Frequency: The business analyst determined the appropriate frequency of engagement for each stakeholder group. Some stakeholders required frequent updates, while others preferred periodic summaries.
- Feedback Mechanisms: The communication plan also incorporated feedback mechanisms to encourage stakeholders to provide input and express any concerns. This helped in addressing issues promptly and fostering a collaborative environment.
By implementing a well-structured communication plan, the business analyst ensured that stakeholders were engaged throughout the software implementation project.
The clear and timely communication facilitated a smooth transition to the new system, minimized resistance to change, and ultimately led to the successful adoption of the software by all stakeholders.
Engagement and Consultation

Effective stakeholder management involves active engagement and consultation with stakeholders to ensure their needs, concerns, and perspectives are taken into account during the project lifecycle.
Business analysts play a pivotal role in facilitating this engagement and consultation process.
They organize regular meetings, conduct surveys, hold workshops, and seek consultations with stakeholders to gather feedback, address issues, and involve them in decision-making processes.
Let’s consider a real-life scenario where a business analyst was involved in a project to implement a new customer relationship management (CRM) system for a retail company.
The stakeholders in this project included the sales team, customer support representatives, marketing department, IT team, and senior management.
To ensure the successful implementation of the CRM system and to address the diverse needs of stakeholders, the business analyst followed these steps for engagement and consultation:
- Stakeholder Analysis: The business analyst conducted a thorough stakeholder analysis to understand the interests, concerns, and expectations of each stakeholder group. This analysis helped in identifying the key stakeholders and determining the most appropriate engagement methods for each group.
- Regular Meetings and Workshops: The business analyst organized regular meetings and workshops with the different stakeholder groups. During these sessions, stakeholders were given the opportunity to provide feedback on system requirements, user interfaces, and reporting functionalities. The business analyst actively listened to their input and ensured that their suggestions were considered during the system design phase.
- Surveys and Consultations: To involve a wider range of stakeholders, the business analyst conducted surveys and sought consultations through one-on-one interviews. This allowed stakeholders who may not have been able to attend meetings or workshops to contribute their perspectives and preferences.
- Decision-Making Involvement: The business analyst ensured that stakeholders were involved in key decision-making processes related to the CRM system implementation. For instance, when selecting a CRM vendor, the business analyst sought input from stakeholders to assess the vendor’s alignment with the business needs and goals.
By actively engaging and consulting with stakeholders throughout the project, the business analyst successfully integrated their inputs, minimized resistance to change, and fostered a collaborative environment. This approach not only resulted in the successful implementation of the CRM system but also increased stakeholder satisfaction and support for the project.
Mitigating Risks: Address any potential risks or concerns raised by stakeholders promptly. Seek to find win-win solutions and demonstrate a commitment to meeting their needs.
Continuous Monitoring

Continuous monitoring of stakeholder sentiments is a crucial aspect of effective stakeholder management.
Business analysts play a vital role in this process by regularly assessing stakeholder attitudes, concerns, and expectations throughout the project lifecycle.
By doing so, they can adapt the communication plan accordingly and ensure that stakeholders are kept informed about project progress and outcomes.
Let’s consider a real-life scenario where a business analyst was involved in a project to implement a new software system for a financial institution.
The stakeholders in this project included the operations team, finance department, IT team, senior management, and external vendors.
The business analyst followed these steps for continuous monitoring and effective stakeholder management:
- Stakeholder Feedback Sessions: The business analyst conducted regular feedback sessions with key stakeholders, including department heads and team leads. These sessions provided a platform for stakeholders to express their concerns, ask questions, and provide feedback on the project’s progress.
- Monitoring Communication Channels: The business analyst closely monitored various communication channels used to update stakeholders, such as emails, project status reports, and team meetings. This allowed them to gauge stakeholder responses and ensure that relevant information was being disseminated.
- Adapting the Communication Plan: Based on the feedback received and stakeholder sentiments, the business analyst made adjustments to the communication plan. They tailored the communication style, frequency, and content to better meet the needs of different stakeholder groups.
- Timely Updates: Throughout the project, the business analyst provided timely updates to stakeholders on milestones achieved, potential challenges, and project outcomes. This transparent approach helped build trust and credibility with stakeholders.
By continuously monitoring stakeholder sentiments and adapting the communication plan accordingly, the business analyst successfully managed stakeholder expectations, mitigated potential risks, and ensured that the project remained aligned with the business objectives.
This proactive approach not only fostered a positive stakeholder experience but also contributed to the overall success of the software implementation project.
Stakeholder management is a crucial aspect of project management and business analysis, ensuring that all relevant individuals and groups are identified, engaged, and their needs are met throughout the project lifecycle.
By adopting effective stakeholder management strategies, business analysts can enhance project success, minimize risks, and foster a collaborative environment where stakeholders feel valued and heard.
At the heart of stakeholder management lies communication and relationship building.
Business analysts must proactively communicate with stakeholders, not only to gather requirements but also to keep them informed about project progress, potential changes, and outcomes.
By actively engaging stakeholders through regular meetings, workshops, and consultations, business analysts can gather valuable feedback and involve stakeholders in decision-making processes, which in turn helps build trust and support for the project.
Additionally, stakeholder management requires a keen understanding of stakeholder interests, concerns, and potential influence on the project.
By conducting stakeholder analysis and categorizing stakeholders based on their power and level of interest, business analysts can prioritize engagement efforts and tailor communication approaches to meet specific stakeholder needs.
This level of responsiveness and consideration for stakeholders’ perspectives contributes to a more positive stakeholder experience and ultimately contributes to the project’s success.
Conclusion On Stakeholder Management
In conclusion, effective stakeholder management is an art that requires empathy, strong communication skills, and a proactive approach from business analysts.
By prioritizing stakeholder engagement, understanding their needs, and keeping them informed throughout the project, business analysts can build strong relationships and pave the way for project success and organizational growth.
Embracing stakeholder management as a fundamental aspect of business analysis can lead to impactful project outcomes and a positive impact on the overall success of the organization.